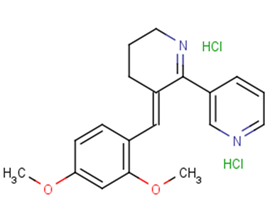
GTS 21 dihydrochloride
CAS No. 156223-05-1
GTS 21 dihydrochloride( DMXB-A | DMBX-anabaseine )
Catalog No. M18083 CAS No. 156223-05-1
GTS 21 dihydrochloride is a nAChRs agonist. nAChRs are neuron receptor proteins that activated by the binding of the neurotransmitter ACh.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 42 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 69 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 105 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 132 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 205 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 309 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 516 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameGTS 21 dihydrochloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionGTS 21 dihydrochloride is a nAChRs agonist. nAChRs are neuron receptor proteins that activated by the binding of the neurotransmitter ACh.
-
DescriptionGTS 21 dihydrochloride is a nAChRs agonist. nAChRs are neuron receptor proteins that activated by the binding of the neurotransmitter ACh.(In Vitro):GTS-21 bound to human α4β2 nAChR (Ki=20 nM) 100-fold more potently than to humanα7-nAChR, and is 18- and 2-fold less potent than (-)-nicotine at human α4β2 and a7 nAChR, respectively.(In Vivo):GTS 21 (4 mg/kg; i.p.; 1, 3, 7, 14 and 21 days) reduces radiation induced histological signs of pulmonary injury.
-
In VitroGTS-21 bound to human α4β2 nAChR (Ki=20 nM) 100-fold more potently than to humanα7-nAChR, and is 18- and 2-fold less potent than (-)-nicotine at human α4β2 and a7 nAChR, respectively.
-
In VivoGTS 21 (4 mg/kg; i.p.; 1, 3, 7, 14 and 21 days) reduces radiation induced histological signs of pulmonary injury. Animal Model:C57BL6 mice were irradiated with 12 Gy to induce a mouse model of Radiation induced lung injury (RILI) Dosage:4 mg/kg Administration:I.p.; 1, 3, 7, 14 and 21 days Result:Reduces lung inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis in radiation treated mice.
-
SynonymsDMXB-A | DMBX-anabaseine
-
PathwayJAK/STAT Signaling
-
TargetSTAT
-
Recptorα4β2 nAChR
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number156223-05-1
-
Formula Weight381.3
-
Molecular FormulaC19H20N2O2·2HCl
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 16.5 mg/mL 43.27 mM
-
SMILESCl.COc1ccc(/C=C\2/CCCN=C2c2cccnc2)c(OC)c1.Cl
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Mol Med. 2014 Jun 19;20:238-47.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Artesunate
Artesunate is a part of the artemisinin group of agents with an IC50 of < 5 μM for small cell lung carcinoma cell line H69.
-
GPA 512
The orally bioavailable prodrug of Galiellalactone, a direct inhibitor of STAT3, prevents the transcription of STAT3 regulated genes.
-
Erasin
A potent, selective STAT3 inhibitor with IC50 of 9.7 uM, inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 with selectivity over STAT5 and STAT1 in cell-based assays.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


